สถิติ เบาหวานในหญิงตั้งครรภ์
การควบคุมอาหารเป็นสิ่งสำคัญที่สุดสำหรับเบาหวานระหว่างตั้งครรภ์ อย่างไรก็ดี คงต้องคำนึงถึงสารอาหารทั้งแม่และลูกด้วย
การรับประทานอาหารตามพลังงานในแต่ละวัน ขึ้นกับน้ำหนักของแม่
· 30 kcal/kg for women with a BMI of 22-25
· 24 kcal/kg for women with a BMI of 26-29
· 12-15 kcal/kg for women with a BMI above 30
ควรรับประทานคาร์โบไฮเดรต ประมาณ 35-45% ของพลังงานจากอาหารทั้งหมดในแต่ละวัน,แบ่งเป็น 3 มื้อ
ไม่นิยมให้น้ำหนักขึ้นมากไปในรายที่น้ำหนักมากอยู่แล้ว เนื่องจากเพิ่มความเสี่ยงต่อลูกตัวใหญ่ คลอดยาก เป็นต้น
The recommended weight gain during singleton pregnancy is dependent on pre-pregnancy BMI: 12.5-18 kg of weight gain for underweight women (BMI <18.5 kg/m2); 11.5-16 kg for normal weight (BMI 18.5-24.9 kg/m2); 7-11.5 kg for overweight (BMI 25-29.9 kg/m2), and 5-9 kg for obese (BMI ≥30.0 kg/m2)
หากคุมอาหารไม่ได้ผลในการควบคุมระดับน้ำตาล แนะนำใช้อินซูลิน
หากน้ำตาลก่อนอาหารสูงกว่า 90-95 มก/ดล ให้ใช้ basal insulin, long-acting insulin analog, or neutral protamine Hagedorn (NPH);
หากน้ำตาลหลังอาหารสูงกว่า 120 มก/ดล ให้ใช้ rapid-acting insulin, or regular insulin
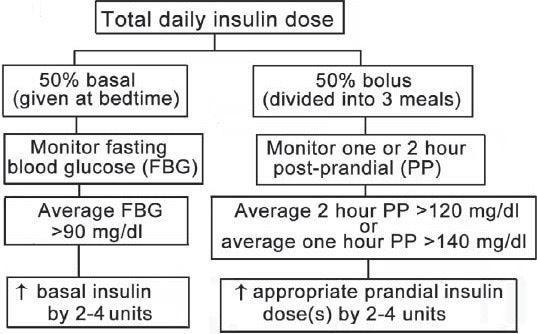
โดยสรุปใช้ยาฉีดก่อนมื้ออาหาร 3 ครั้ง และก่อนนอน 1 ครั้ง a 4-injections-per-day regimen “basal and meal time insulin regimen”
For overt diabetes with pregnancy in the first trimester, the total daily insulin requirement is 0.7 units/kg/day, in the second trimester it is 0.8 units/kg/day, and in the third trimester it is 0.9-1.0 units/kg/day
In a morbidly obese woman, the initial doses of insulin may need to be increased to 1.5-2.0 units/kg to overcome the combined IR of pregnancy and obesity. Subsequently, the calculated total daily dose of insulin should be divided into 2 halves; one half given as basal insulin at bed time, and the other half divided between 3 meals, and given as rapid-acting, or regular insulin before meals. As insulin requirement may increase with the progression of pregnancy, it is crucial to follow patients’ SMBG regularly, and optimize their insulin doses.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4404472/