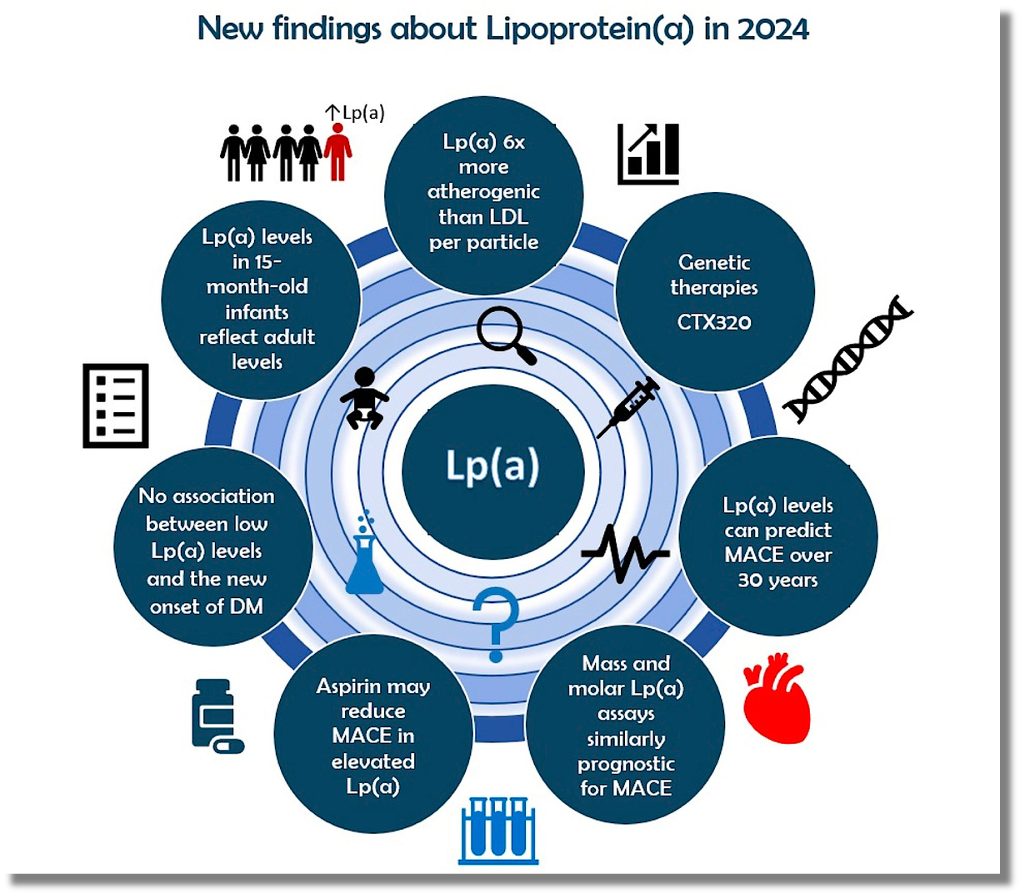
ไลโปโปรตีนลิตเติ้ลเอ lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] เป็นปัจจัยสำคัญอีกปัจจัยหนึ่ง ถือเป็นปัจจัยอันดับ 4 รองจาก ไขมัน ความดันโลหิต และบุหรี่ ในการส่งผลต่อการเกิดโรคหัวใจและหลอดเลือด (CVD) จำพวก ASCVD, aortic stenosis/CAVD, ischemic stroke, peripheral arterial disease (PAD), heart failure, และ atrial fibrillation เป็นต้น
โดยเกิดจากหลายกลไก ดังนี้ the proatherogenic effects mediated by apoB, a pro-inflammatory response driven by OxPL, and pro-thrombotic effects resulting from the antifibrinolytic properties of apo(a) and its interactions with platelets นอกจากนี้ยังมีปัจจัยอื่น เช่น endothelial dysfunction, inflammation, lipid accumulation, and calcification ทำให้เกิด ASCVD และ calcific aortic valve stenosis (CAVS) อีกด้วย
หากระดับ Lp(a) levels (≥ 50 mg/dL or ≥ 125 nmol/L) ถือว่า high risk ต่อการเกิด CVD และหากมากกว่า 180 mg/dL (>450 nmol/L) บ่งถึง very high risk
https://www.archivesofmedicalscience.com/pdf-202213-122760?filename=2024_%20The%20Year%20in.pdf